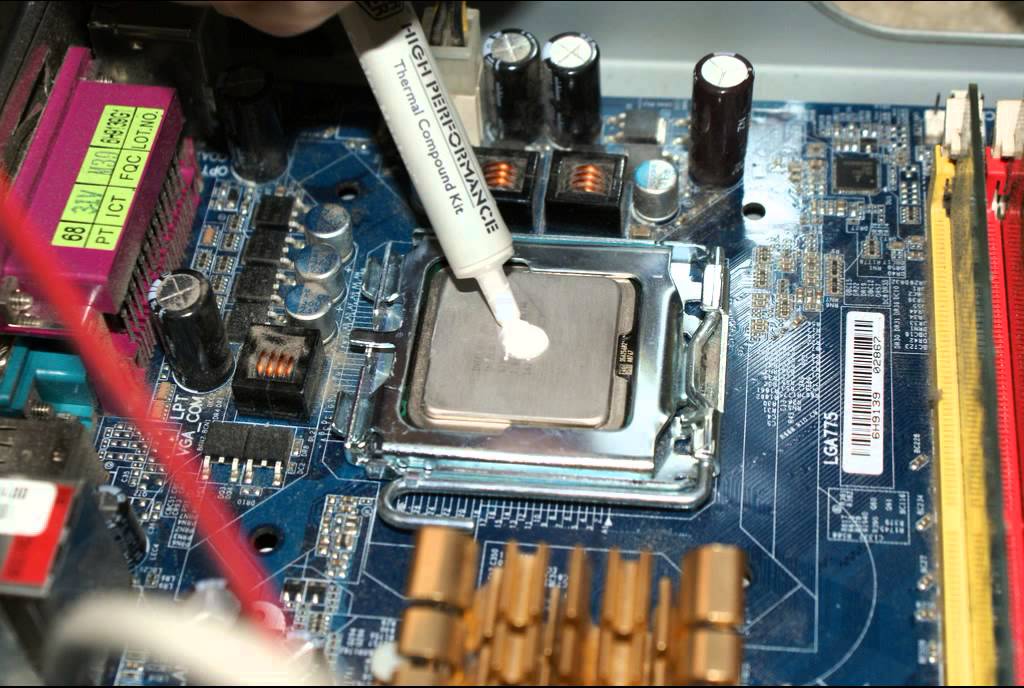
Thermal compound is a substance that helps facilitate heat transfer between the CPU and its heat sink. Without it, the heat sink would have a much smaller effective surface area for dissipating heat.
It is applied between the microprocessor and the heat sink to eliminate air gaps that reduce thermal conductivity. There are a few different types of Thermal Compound.
Non-silicone
Non-silicone thermal greases are used for the interface between components where silicone contamination is a concern. They are formulated with polysynthetic oils and contain thermally conductive fillers. They have low bleed, low resistance and can be applied using stencils or automated applications. These products are ideal for thin bond lines and provide a wide temperature range for reliable performance.
They are also easy to apply and can be wiped off using a clean cloth or paper towel. They do not harden or crack, and have a low shrinkage that minimizes the risk of damage to delicate components.
The global market for non-silicone thermal grease is expected to grow at a moderate rate over the forecast period. The growth is largely driven by the growing adoption of strategies by key players. These companies are focusing on increasing their product portfolios and capabilities, and improving their presence in an accelerating industry. Moreover, they are investing in R&D to enhance their position and expand their market reach.
Conductive
A conductive thermal compound is comprised of metal particles that offer both high heat transfer and electrical conductivity. This type of thermal compound is used to fill in the microscopic gaps between the CPU and the IHS. This helps maximize the contact surface area and promotes proper cooling. The most common conductive thermal pastes include zinc, copper and silver.
Most thermal compounds are composed of a bonding material and a filler. The bonding materials can be various types of silicones, urethanes and acrylates. The filler is typically a variety of metals, including silver, aluminum, copper and exotic oxides. The highest performing liquid metal thermal compounds contain a mixture of silver, gallium, indium and tin.
Regardless of the type of thermal paste you choose, it is essential that you use only a small layer to ensure proper cooling. Excessive thermal paste will act as an insulator and will prevent the heat from dissipating properly. To apply a thin layer, simply rub the compound onto the top of your CPU using a credit card or other flat object with good stability.
Ceramic
Usually composed of silver, aluminum or copper particles in a silicone base, they provide high heat conduction and low thermal expansion. They can also resist corrosion and erosion. However, they can be electrically conductive and capacitive which could cause malfunctions or even damage if they come into contact with electronic components.
They are generally a bit cheaper than ceramic pastes but they have a much lower thermal conductivity than metal-based compounds. They also have a tendency to dry out quickly.
Liquid-metal CPU thermal compound has a low risk of part damage and is easy to apply, but it can still be difficult for beginners to use correctly. It is also dangerous to spill if it hits the processor pins or motherboard components, and it can lead to short circuits in case it seeps into other parts of the system. It’s a good idea to stick with ceramic-based thermal compound if you’re not confident in your skill at applying it.
Carbon
A high-quality thermal compound can help improve heat conduction between a processor and its heat sink, making it more efficient. It can also help increase the speed of the CPU and improve overall system performance. It is available in a variety of viscosities, allowing for customization to suit different applications.
This product from Arctic is considered a top pick by many reviewers and offers an excellent value for its price. It features a unique formula that guarantees exceptional heat dissipation and stability needed for overclocking. It is metal-free and non-electrical conductive, ensuring that it will not cause any damage to the CPU or GPU.
It comes in a small tube with a syringe tip for precise application. The tip makes it easy to apply a small dab to the center of the processor, which Maximum PC recommends should be about the size of a pea or BB. This ensures a uniform spread and allows the user to avoid leaving any excess on the edge of the processor, which could lead to the formation of air bubbles.